Back to: Robotics & Artificial Intelligence (Class IX)
Robot
A robot is a machine designed to perform tasks automatically, either by following pre-programmed instructions or by responding to inputs from its environment. Robots can be controlled by computers or operated autonomously, using sensors and artificial intelligence to make decisions.
Benefits of Robot:
- In many situations robots can increase productivity, efficiency, quality and consistency of products.
- Unlike humans, robots don’t get bored.
- Until they wear out, they can do the same thing again and again.
- They can be very accurate – to fractions of an inch (as is needed for example in manufacturing of microelectronics)
- Robots can work in environments which are unsafe for humans – in the nuclear or chemical industries.
- Robots don’t have the same environmental requirements that humans do – such as lighting, air conditioning or noise protection.
- Robots have some sensors/actuators which are more capable than humans.
Evolution of Robot
Industrial robots are not usually humanoid in shape, although they are capable of reproducing human movements and behaviour but with the strength, precision and speed of a machine. The first industrial robots were developed by George Devol, American inventor and founder of the first robotics company in history: Unimation.
In 1954, what is considered the first industrial robot was developed in the USA: a hydraulic arm called Unimate, used to lift heavy loads, which was sold to General Motors. In the following years they developed several versions of the same model of the company Unimation that were introduced, little by little, in some factories mainly in the automotive sector.
Law of Robotics
The Three Laws of Robotics’ (often shortened to The Three Laws or known as Asimov’s Laws) are a set of rules devised by science fiction author Isaac Asimov.
First Law
A robot may not injure a human being or, through inaction, allow a human being to come to harm.
Second Law
A robot must obey the orders given it by human beings except where such orders would conflict with the First Law.
Third Law
A robot must protect its own existence as long as such protection does not conflict with the First or Second Law.
Classification of Robots
1. Aerial Robots: These robots are designed to operate in the air or fly. They include various types such as drones, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), and autonomous flying robots. Aerial robots are commonly used for surveillance, aerial photography, search and rescue missions, and package delivery.
2. Ground Robots: Ground robots are designed to operate on land surfaces. They can have wheels, tracks, or legs for locomotion. Examples of ground robots include robotic vacuum cleaners, rovers used in space exploration, autonomous cars, and agricultural robots used for farming tasks.
3. Underwater Robots: These robots are designed to operate underwater and are commonly referred to as underwater autonomous vehicles (UAVs) or underwater drones. They are used for marine exploration, underwater inspections, oceanographic research, and deep-sea exploration. Underwater robots are equipped with special features to withstand the high-pressure environment and have propulsion systems suitable for underwater.
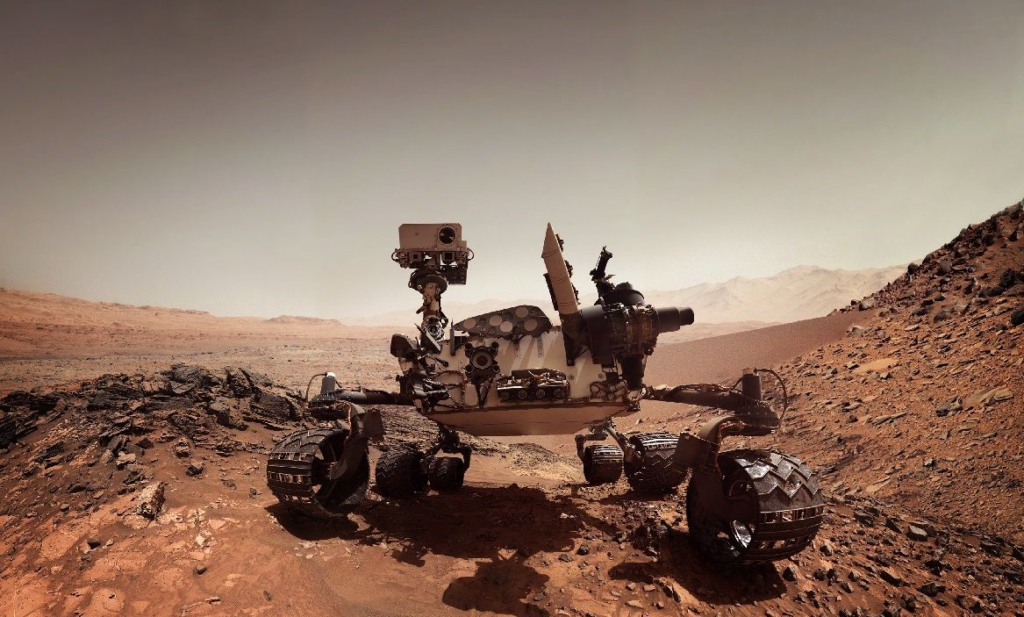
4. Space Robots: Space robots are designed to operate in outer space or planetary surfaces. They are used for various tasks such as satellite maintenance, space exploration, and extraterrestrial research. Space robots can be remotely operated or autonomous, and they are built to withstand the extreme conditions of space, including vacuum, radiation, and microgravity.
5. Humanoid Robots: Humanoid robots are designed to resemble and interact with humans. They are equipped with human-like features such as arms, legs, and a head. These robots are used in research, entertainment, healthcare, and assistance applications. Humanoid robots aim to mimic human movements and behaviors, enabling them to perform tasks that require human-like dexterity and interaction.
It’s worth noting that some robots can be designed to operate in multiple fields or terrains. For example, there are robots that can function both in the air and underwater, known as amphibious robots. Similarly, there are robots designed for space exploration that can also be used on planetary surfaces.
Real World Application of Robot
The Robotics domain is a combination of science, technology, and engineering. The main aim of robotics is to manufacture intelligent machines. The first step of building a robot is the mechanical construction of the structure as per need. This structure is powered by electrical circuitry and is finally controlled by computer programming. These machines serve to be a perfect helping hand and are used for a versatile group of applications including entertainment, defence, medicine, household, etc
Entertainment
A very popular application of robotics lies in the entertainment sector. Robotic toys are very captivating and attract young minds. They provide a number of features that help the child to learn and enjoy simultaneously. Such products give rise to curiosity and build interest in the technology domain.

Household
Robots are specifically designed to reduce human efforts. With the development of technology, we have been provided with a lot of devices that are fully automated and are convenient to use. In households, robots, like cooking bots, lawn-mower, and vacuum bots, have proved to be super helpful assistants. They provide great ease and comfort to consumers by completing the task given to them quickly and effortlessly. These Robots are supported by Artificial Intelligence, a technology that allows them to practice machine learning for improved operation.

Industries
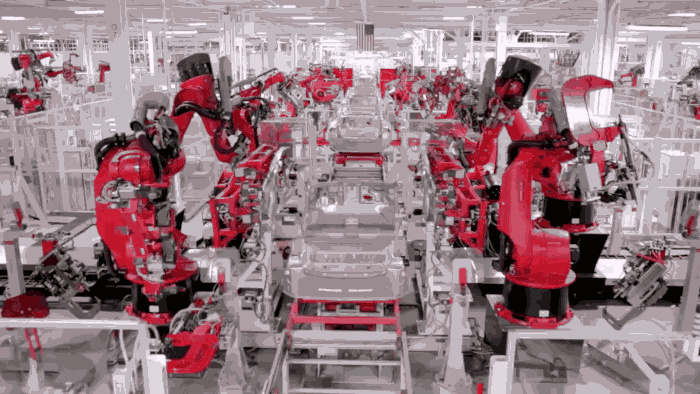
Initially, product manufacturing used to be a tedious task that required a huge workforce. It was difficult to manage the production speed as during the old days every task was handled manually; however, with the advancement of technology, a number of tasks that required physical participation have been replaced by machines. Robotic arms are also employed in applications that require a task to be done in a repeated fashion such as nut-bolt fastening, brand-label wrapping, etc.
Defence
Defence and related departments such as logistics and supply management, intelligence surveillance and reconnaissance, cyber operations, etc. make use of robots on a large scale. These intelligent devices are used to control the missiles, locate snipers, survey the enemy area, etc. Surveillance bots are the most popular robots used in military applications.

Medicine
Robots can be a great assistance tool for doctors. Robotic equipment, being used in a hospital, provides a 3-Dimensional view, 10 fold enlargement of the surgical area, and instruments that are superior to the mobility of a human hand. The Medical field requires great precision and accuracy. In the modern era, traditional surgeries are getting replaced by robotic surgeries because machines are less prone to human errors such as slipping of the surgical blade from hands during an operation that might put the patient’s life at stake.

Education
A lot of students have to skip their studies upon getting affected by disease-causing germs. With the assistance of robotics, a sick child is provided with the facility of attending the classes virtually. A number of autistic kids are uncomfortable conversing with people, and in such situations, a robot is considered to be of great use as it creates a friendly atmosphere and assists the child to converse and learn better.

Transportation
Amazon and other related shopping sites have escalated their service quality by upgrading their manual delivery systems to robotic package delivery systems. The robotic delivery systems are comparatively safe, less time consuming, and require less manual power for operation. The delivery bot is equipped with face recognition and object detection that helps it to avoid obstacles and hand over the parcel to the concerned keeper.

Safety
Robots are advantageous as they can be freely used in dangerous places and avoid putting human life at risk. They are basically used in locations that are hard to reach or are prone to health hazards and accidents. For example, it is dangerous for humans to survey an area where landmines are planted; however, if the same place is surveyed with the help of a lifeless robot, it is comparatively easier and comfortable.

